To the monocotsare plants angiosperms that have only one cotyledon in their embryo, roots fasciculate and parallel veins.
We prepared a list of exercises on monocots so you can test your knowledge about this group of angiosperm plants.
see more
Biology teacher fired after class on XX and XY chromosomes;…
Cannabidiol found in common plant in Brazil brings new perspective…
You can consult the feedback and save this list of exercises in PDF at the end of the post!
1) (UFLA) Mark the alternative that contains characteristics only of monocotyledons.
a) Leaves with parallel veins, diffuse liberoligneous stem bundles, trimerous flowers and fasciculate roots.
b) Leaves with parallel veins, ordered liberoligneous bundles of the stem, pentamerous flowers and fasciculate roots.
c) Leaves with branched veins, ordered liberoligneous stem bundles, trimerous flowers and axial roots.
d) Leaves with branched veins, ordered liberoligneous stem bundles, trimerous flowers and fasciculate roots.
2) (UFRGS) Monocots and eudicots can generally be differentiated:
I – By the type of climate in which they develop.
II – By the characteristics of the leaves, stems and roots.
III – By the structures of the seeds.
Which ones are correct?
a) I only.
b) II only.
c) III only.
d) Only II and III.
e) I, II and III.
3) (UDESC) A student needed to organize his school's botanical collection and separate the plants into monocotyledons and dicotyledons. So he selected rice, wheat and corn plants, which were correctly placed in a group; while beans, soybeans and peas were placed in another group. Analyze the propositions in relation to the characteristics of monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plants and mark (T) for true and (F) for false.
( ) The roots of monocots are fasciculate (hair) and found in rice, wheat and corn plants.
( ) The leaves of eudicots have parallel veins and can be seen in bean and soybean plants.
( ) Monocot seeds are made up of two cotyledons and are found in wheat plants.
( ) The flowers of eudicotyledons generally have floral parts in the number of three or multiples of three and are common in corn and wheat plants.
( ) The leaves of monocotyledons are made up of reticulate, or branched, veins, and are observed in rice and corn plants.
Tick the alternative that contains the correct sequence, from top to bottom.
a) F-F-T-F-V.
b) V-T-F-F-F.
c) F-T-T-T-F.
d) F-T-F-T-F.
e) T-F-F-F-F.
4) (UECE) With the aim of solving the problem of erosion on his property, a farmer bought plant seedlings recommended by a biologist. These seedlings have fasciculated roots, parallel veins and trimerous flowers, therefore, they are representatives of:
a) legumes.
b) ferns.
c) cycads.
d) grasses.
5) (URCA) Another unprecedented paleontological discovery was announced at the headquarters of Geopark Araripe. An unpublished fossil find of 120 million years. A plant from the Cretaceous Period popularly known as Japecanga, from the Smilacaceae family. The given name is a tribute to Professor Jackson Antero (in memory), Cratosmilax jacksoni. Smilacaceae is a family of basal monocotyledonous plants that occur on all continents and is related to the origin of flowering plants. Diário do Nordeste, 01/22/2015.
Regarding this division of plants, the monocotyledons, it is incorrect to state:
a) in this group there are plants with nodes and internodes in the stem.
b) in this group there are plants that reproduce by means other than seeds.
c) flowers usually have a trimerous base.
d) the leaves are usually parallel-innerve.
e) Seeds usually have two cotyledons.
6) Some characteristics help to identify a monocot. Analyze the alternatives below and mark the one that indicates a characteristic that is not found in monocots.
a) Leaves with parallel venation.
b) Trimerous flowers.
c) Embryo with one cotyledon.
d) Stem with bundles arranged in a ring.
e) Bundled roots.
7) (URCA) Palms are monocots found in tropical areas all over the world. Examples of palm trees typical of the northeastern caatinga are:
a) babassu and catole.
b) licuri and coconut tree.
c) catingueira and catolé.
d) carnaúba and macaúba.
e) imperial palm and coconut palm.
8) Monocotyledons are a group of plants that have grasses as representative. Monocots are:
a) bryophytes.
b) pteridophytes.
c) gymnosperms.
d) angiosperms.
e) eudicots.
9) A student collected a beautiful flower and asked his teacher what feature might suggest that it was a monocot. Mark the alternative that indicates the teacher's correct answer.
a) Flowers of monocots are usually dimerous.
b) Flowers of monocots are usually trimerous.
c) Flowers of monocots are usually tetramerous.
d) Flowers of monocots are generally pentamerous.
10) (UPE) An amateur naturalist, interested in plants, could start his studies with Angiosperms, because of the wide distribution of species in the world. Some features allow dividing them into two classes. Thus, the naturalist could explore a fruit, cutting it in half and looking for the number of cotyledons, two or one, dicotyledonous or monocotyledonous, respectively. In addition to these characteristics, other differences can be observed below:
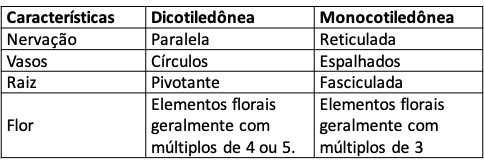
They are correct:
a) I and II, only.
b) I, only.
c) I, II, III and IV.
d) II, IV, only.
e) II, III and IV, only.
1 – the
2 – d
3 – and
4 – d
5 – and
6 – d
7 – d
8 – d
9 – b
10 – and
Click here to save this list of exercises on monocots in PDF!
Read too: