porifera, or simply sponges or spongiary, are types of invertebrate animals aquatic and fixed in the substrate. Its nomenclature is linked to the presence of pores on its body.
belonging to phylum Porifera, their shapes, sizes and colors are varied. However, the body pattern is basic, shaped like a vase, tube or barrel.
see more
Biology teacher fired after class on XX and XY chromosomes;…
Cannabidiol found in common plant in Brazil brings new perspective…
There is a belief that the porifera arose during the Lower Cambrian period, about 500 million years ago. Furthermore, documents detail that sponges were already known since the treaty of classification of living beings, performed by Aristotle.
However, until the beginning of the 18th century, poriferans were seen only as plants.
It is understood that there are more than 10,000 species of sponges all over the world. And in the Brazilian scenario alone, more than 300 species.

Most species of sponges live in marine environments, few in fresh water. Therefore, they are located trapped in the bottom of the sea, in the sand, in rocks and shells. They can live both solitary and in colonies.
The poriferans have walls perforated by pores, and, in their inner part, there is a cavity named as atrium or spongiocoel.
The osculum is the opening located at the end opposite the base of your body. On the outside, they are surrounded by pinacocytes, cells found and united. And that outer wall is named pinacoderm.
Its skeleton is internal and contains calcareous or siliceous spicules. Furthermore, it can also be organic and made up of collagen fibers – the spongins.
Sponges are absent from a nervous system and fabrics. Choanocytes, ovoid and flagellated cells make up its internal cavity.
The movement of flagella enables their circulation and synthesizes the circulatory system of sponges. There are even amebocytes. These are free cells existing between the layers of pinacocytes and choanocytes.
The phylum Porifera is classified into three classes, according to their cellular organization and the characteristics of the spicules:
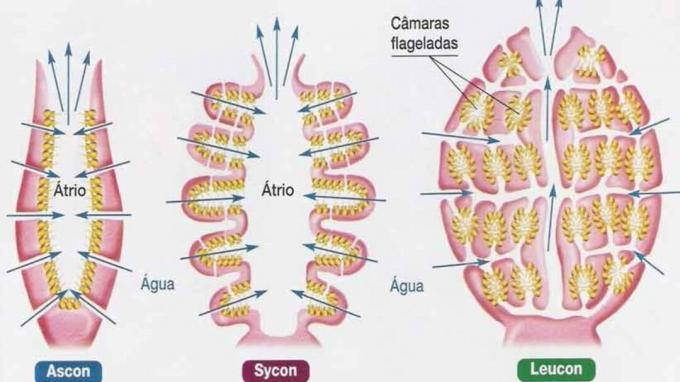
there are three types of sponges, which are distinguished by their complexity, are: ascon, Sicon and Leucon.
Ascon are the simplest sponges, similar in appearance to hollow cylinders. They have an opening at the upper end called an osculum.
Asconoids have their outer part surrounded by two types of cells – pinacocytes and porocytes. The inner part, spongiocoel, is composed of choanocytes.
Syconoids, or simply sycon, are more complex sponges.
They have the thickest wall, where the cracks are located in which water enters the internal environment, being conducted to the afferent channels.
In this place, locate the porocytes.
The third and last type are the leuconoid sponges.
Characterized as larger and with a complex body structure, they have slits that conduct water to afferent channels.
Its reproduction can be both asexual and sexual.
In the case of the asexual, it results from fragmentation, budding and, also, through the constitution of the gemmule – a formation structure.
Sponges are characterized as filter feeders, promoting respiration through gas exchange by diffusion.
However, their diet consists of absorbing food particles dispersed in water, as is the case with protozoa and unicellular algae.
Read too: