
Absolute frequency and relative frequency are two very useful concepts in data analysis and Statistic.
The absolute frequency corresponds to the number of observations in each class of a variable. The relative frequency is given by dividing the number of observations in each class by the total number of observations.
see more
Students from Rio de Janeiro will compete for medals at the Olympics…
The Institute of Mathematics is open for registration for the Olympics…
To really understand what absolute frequency and relative frequency mean and how to calculate, consider the following example:
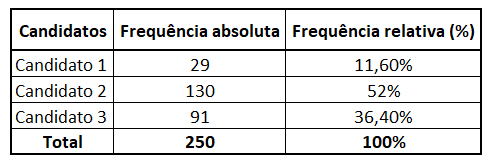
To assess the intention to vote for mayor in a certain municipality, a survey was carried out with 250 voters. There are three candidates for mayor and each voter answers which one he intends to vote for.
After obtaining the data, count how many voters intend to vote for each of the three candidates, obtaining the absolute frequency for each candidate:
Dividing each quantity by the total number of voters, we get relative frequency for each candidate:
For ease of interpretation, relative frequency is usually presented as a percentage, so we multiply each result by 100%.
We can organize this data into a frequency table:
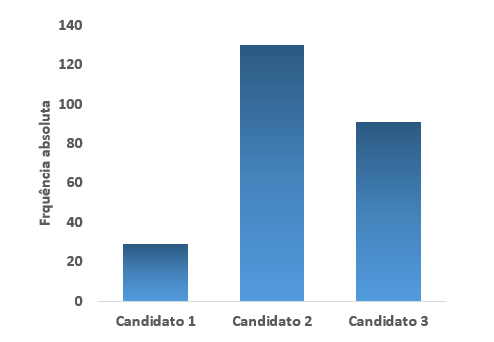
Also, for a better visualization and understanding of the data, we can use some graphics.
In the bar graph, each bar represents a class and its size indicates the absolute frequency corresponding to the class.
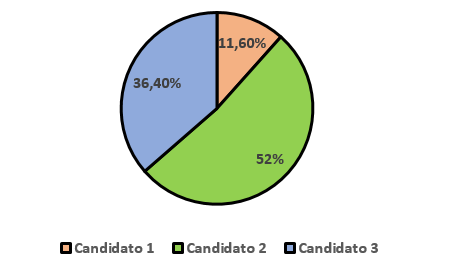
At the pie charts or “pizza”, each sector represents the class in relation to the whole, that is, in relation to the total number of observations. Generally, the relative frequency in percentage is also used here.
You may also be interested:
