At ecological pyramids or trophic pyramids is one of the most important issues in biology and of great importance for the identification of the types of trophic levels of the food chain and its relationships in a community, they graphically represent the flow of energy and matter along a food chain of diverse species, such as numbers, mass, and energy.
Ecological pyramids, as mentioned, are pyramids that represent the flow of energy and matter in a chain. food, these pyramids can be of 3 different types: numerical pyramid, biomass pyramid and pyramid of energy. Let's know where one of them is?
Before, it is important to emphasize that in a given food chain, there are different species of organisms that carry out the so-called photosynthesis, that is, that they produce their own energy without needing other species to do so, at trophic levels they are called producers, producers in the food chain they always occupy the first trophic level, followed by organisms that feed on the producers, that is, herbivores, the herbivores are called consumers primary and are in the second trophic level, followed by carnivores, located in the third trophic level, that is, secondary consumers, and so on. against
Here's the graphic image as an example:
Numerical pyramid: The numerical pyramid or pyramid of numbers, as the same name induces, indicates the number of individuals, that is, of species in each trophic level in a food chain. In a food chain on the part of producers, there can be more than 5,000 producing plants in the first trophic level, these plants serve as food for the snails that are other types of species, these snails in an ecological pyramid, can have an average of 300 of them, the robins come right after and feed on the snails, that is, 5 robins in the ecological pyramid feed on 300 snails, and finally, the robins will serve as food for only 1 hawk inside the pyramid numerical. In these cases, the inverted pyramid may occur:

In this situation, the pyramid is inverted, because as we can see it starts thin, that is, it starts with an ipe, a kind of tree that serves as food for 1000 beetles, this pyramid becomes expands, but then decreases, as only 20 birds enjoyed these 1000 beetles, that is, the pyramid is inverted, in these cases there are few producers, such as the ipe, which is on the first level trophic.
Biomass Pyramid: The biomass pyramid, as the name implies, indicates the body mass in each of the trophic levels, this body mass is measured as dry mass, this dry mass is measured by (g/m² or kg/m²) And how is this made measurement? When ecologists enter the measurement process, that is, a mass analysis within a trophic level, they take an area, which can be more or less than one meter square, in this square meter, curettage of all the plants in that area is done, these plants are taken to a greenhouse and stay for a while in that place, during this time the plants evaporate the water they contain within their leaves, that is, the plants become dry, thus measuring the biomass of that level species. trophic.
We also recommend: Protocooperation
The biomass pyramid can also be inverted, but this only occurs in aquatic environments such as oceans and lakes, for example:

Phytoplankton at trophic levels are producers, as these types of algae can carry out photosynthesis like other plants of other species, in terms of biomass, there is less mass in phytoplankton than zooplankton, as we can see in the image the biomass of primary consumers is greater than that of producers, and how is this possible? In the aquatic environment, phytoplankton reproduce very quickly, even though the biomass is at a lower level, they are always reproducing, that is, they multiply quickly.
Energy Pyramid: It is the most important pyramid among the others. See the example:
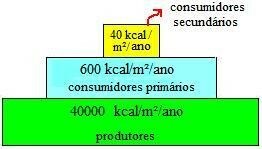
This style of pyramid indicates the amount of energy stored in each trophic level, the same is the the only one that does not exist in inverted form, as energy cannot be recycled, it is always unidirectional. It can be transformed, but never created or destroyed. It is the most complex pyramid of all. In the food chain, the energy flow decreases according to the height magnitude of the trophic levels, it decreases at higher trophic levels, as is the case in image shown above, that is, if the food chain is of a short species, the energy will be used more quickly and so it will happen in other chains food.
Very nice to know the species of ecological pyramids, isn't it? And the nicest thing is that it can be included in a fun and interactive way in the classroom, especially in biology classes. The pyramids can be made by hand by the students themselves with the help of the teachers, so the students during the activity will have more knowledge and interaction with the subject discussed, each building their ecological pyramid, whether numerical, biomass and energy, following the guidelines of the teacher.
Subscribe to our email list and receive interesting information and updates in your email inbox
Thanks for signing up.