We selected in this post suggestions for Annual planning for 1 year of elementary school.
A key element of effective teaching lies in planning teaching and learning activities carried out at school, particularly in the classroom. This planning must be done for each day of class and is part of the teacher's professional responsibilities.
Without it, learning objectives are meaningless. Therefore, a lesson plan must contain, even if in a summarized way, the teacher's pedagogical decisions about what to teach, how to teach and how to evaluate what he taught.
See too:
A lesson plan should not be expected to work in the same way for different teachers. It is an individual work instrument and must be developed to achieve the objectives of each class, separately.
And in this post we selected some ideas and suggestions to serve as a model “Annual Planning 1 year of Elementary School”.
Index
This wonderful material was prepared by (CEVIVA) check the following link and download it in PDF with 36 pages:
Valuing the importance of caring for the health of one's own body, for the need for care with hygiene, nutrition, accident prevention, vaccination, physical activities and leisure.
The student should know valuing their creativity in seeking and trying to solve situations. Daily assessment by observing the performance of oral and written activities. Activities in the notebook and group work.
Environment, Health, Ethics, Cultural plurality, Special education, Local issues, Consumption.
Provide students with access to the literate world, building the literacy and literacy process, with a pedagogical action aimed at concrete situations that are significant to the students' reality, in a pleasurable and playful.
The student should value their creativity in seeking and trying to resolve situations. Daily assessment by observing the performance of oral and written activities. Activities in the notebook and group work.
Cultural plurality, Special Education, Local Themes, Consumption, Values, Health, Ethics.
Magazines, books, scissors, Popsicle sticks, scraps, dice, colored pencils, letter games, syllables, words and phrases, paintings, music, sound, newspapers, gouaches, pieces of E.V.A, papers of different colors, buttons.
Provide the development of the child's perception and the discovery of a logical world, full of relationships, mathematical expressions and concepts such as: colors, numerals, numbers, calculations, among others, developing agility mental.
SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES
Mathematics is fundamental for the apprehension of concepts of any kind and for the development of several skills, such as:
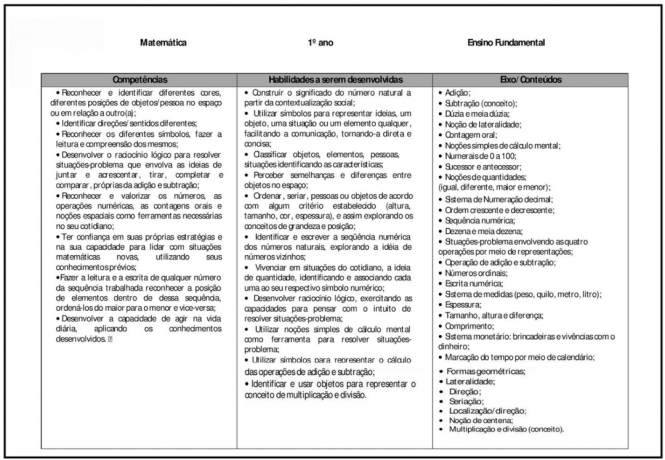
Learning to count; • Natural numbers 99 (minimum) • Ascending and descending order • Addition – Problems • Decimal numbering system • Subtraction Problems • Dozen • Odd and even numbers; ordinals (first, second, etc.); • Our money; • exact hours; • Geometry
The student should know: recognize the numerical order as well as memorize the basic facts of the operations, valuing their creativity in seeking and trying to solve problem situations. Daily assessment by observing the performance of oral and written activities. Activities in the notebook and group work.

Recognize and contextualize the environment in which the student lives. Identify how people build their lives in family relationships, work, artistic activities, religiosity and other instances that give meaning to their existence.
The student should know valuing their creativity in seeking and trying to solve situations. Daily assessment by observing the performance of oral and written activities. Activities in the notebook and group work.
Health, Cultural Plurality, Values, Ethics, Sexual Orientation, Special Education, Local Issues, Consumption.



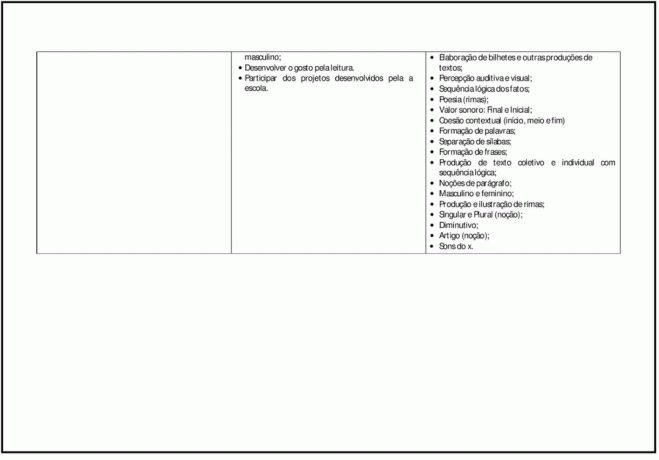



The teaching of Portuguese Language privileges the development of the ability to listen, speak, read and write and present the production and interpretation of oral and written texts in different situations of use, without discrimination of linguistic variations, having the transversal themes as a source of entertainment, obtaining knowledge and elements of support.
Provide opportunities for the child to express feelings, ideas, opinions and experiences, as well as valuing and recognize the greatness of the variety of texts that circulate in spaces, and their importance to obtain information.
To value reading as a source of entertainment, pleasure, information, advertising, establishing relationships, arguing, concluding and evaluating, thus contributing to their formation of citizens and agents of change of reality.
It must be continuous and daily, as well as relying on an instrument throughout the process, which leads the student to reflect on writing and reading.
We must be at the service of the student's learning, for that the teacher must follow the process of development, noticing their advances and making records of writing to forward new interventions pedagogical.
Mathematics was built in a continuous and accumulative process, forming a body of knowledge, acquiring reasoning, abstractions and registers. Thus, the teaching of mathematics must not be outside the historical, social and scientific context, providing the meaning of symbols, records, procedures, ideas and reasoning.
The assessment takes place according to a criterion and this must be linked to a content, as well as the planning and teaching methodology aims to develop in the student, reasoning, reflection and establishment of relationships on the part of the teacher for a better training of the student. It must occur throughout the process, with no space to be performed only at certain times.
The study and teaching of stories are directed towards the development of critical learning of the human movements in their due time and places, in a vision that respects the culture of each character in the story. It also promotes a series of discussions and research on current issues that are part of the historical culture of Brazilian society as well as other peoples and nations.
We can say that history should lead the student to understand the historical process, establishing a relationship between the past and the present, with a view to the formation of a critical and participating student, discussing, comparing, identifying and enlarging.
The purpose of the Science proposal is the transmission of knowledge that enable the student to understand the world in which they live, or that is, he must appropriate information, study and reflect on the actions according to the needs that ensure his survival.
The objective of the Science proposal is the transmission of knowledge that enables the student to understand the world in which they live, or that is, he must appropriate information, study and reflect on his actions, according to the needs that ensure his survival. In this perspective, the assessment should be daily related to the content and methodology loved.
Geography as Science studies geographic space, understood as products of the relationship between human beings and the environment, it is the result of the forces of transformation of human actions on the environment.
In this way, we educators must opt for a critical geography that explains the geographic space with the social space constructed at all times in history.
Know the organization of geographic space and the functioning of nature in its multiple relationships, of in order to understand the role of societies and their construction in the production of the territory of the landscape and the place.
It is up to the teacher to awaken in the students the taste for a science that contributes so much to the formation of fully aware, participative, responsible and committed citizens.
Observing the performance of each one regarding the domain and use of concepts, categories, information related to geographic knowledge.
Check if the student is capable:
Subscribe to our email list and receive interesting information and updates in your email inbox
Thanks for signing up.
