Math Activities 5th year of Elementary School – To Print.
We have selected excellent suggestions from this post. 5 year Math Activities, elementary school, ready to print and apply in the classroom or as a homework assignment.
are excellent math educational activities for 5th year to print.
Index
Hi, we've decided to update the post to better meet our users' needs.
Check out below Math Activities for students of 5th (fifth) year of elementary school.
Proportionality, for mathematics, chemistry and physics, is the simplest and most common relationship between quantities. Direct proportionality is a mathematical concept widely used in the lay population because it is very useful and easy to solve through the “rule of three”. Wikipedia
Working units and tens with students from the fifth year of elementary school, math activities to print.

See too:
5-year Math Activity: Combining numbers that result in a sum.


Addition is one of the basic operations of arithmetic. In its simplest form, addition combines two numbers into a single number, called a sum, total, or result.
How about stimulating your students' creativity with these activities on geometric shapes?
Objectives of these activities:


This activity encourages creativity and encourages teamwork. Its main objective is to encourage knowledge of the measures.
Check out the specific goals:
For this activity we will need the following materials:

Check out a wonderful activity to work the Monetary System, with students from the fifth year of elementary school.
The (our money activity) has the following objectives:

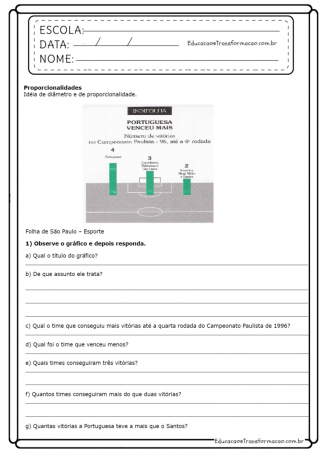
let's work "Diameter and Perimeter" with 5 year students?
The diameter of a circle is given by any string that passes through the center of the figure.
The perimeter is the measure of the outline of a two-dimensional object, that is, the sum of all sides of a geometric figure.

Check out several suggestions for activities and assessments of Mathematics 5th year in PDF.
Would you like teach math to your students, but is it difficult to find a way to hold the children's attention?
The following activities will help you teacher in the teaching-learning process, check it out:
Use the notebook to develop the activities. Copy, read and solve in notebook.


D1 - Identify object location/movement on maps, sketches and other graphical representations.
D2 – Identify common properties and differences between polyhedrons and round bodies, relating three-dimensional figures with their unfolding.
D3 – Identify common properties and differences between two-dimensional figures by the number of sides, by types of angles.
D4 – Identify the quadrilaterals observing the relative positions between their sides (parallel, concurrent, perpendicular).
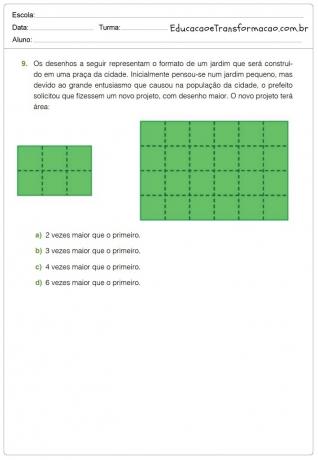
D5 - Recognize the conservation or modification of measures of sides, perimeter, area under expansion and/or reduction of polygonal figures using gridded meshes.
Basic Contents: Plane Geometry; and Spatial Geometry.

Note the location of the car and answer:

Figure 1 below represents the unfolding of figure 2, the cube.
This flashlight battery has approximately the shape:
In one of the math classes, I learned about polyhedra and round bodies. Then I went to the supermarket. There I bought a box of washing powder, a can of oil and a ball. At the checkout I noticed that the three products had, respectively, the form of:


The comparison of quantities of the same nature that gives rise to the idea of measurement is very old. The measurement was based on the dimensions of the human body, in addition to highlighting curious aspects such as the fact that, in certain civilizations, the measurements of the king's body were taken as a standard.
For certain applications, measures were used that, over time, became conventional. Velocity, time and mass are examples of quantities for which some measurements have been agreed. Thus, it is important that students recognize the different situations that lead them to deal with physical quantities, so that they can identify which attribute will be measured and what the measurement means.
The student must understand that measures can be agreed or that conventional systems can be used to calculate perimeters, areas, monetary values and exchange of coins and banknotes
D6 - Estimate the measurement of quantities using conventional or non-conventional measurement units.
D7 – Solve the significant problems using standardized measurement units such as km/m/cm/mm, kg/g/mg, l/ml.
D8 - Establish relationships between time measurement units.
D9 – Establish the relationships between the start and end times and/or the duration interval of an event or event.
D10 - In a problem, to establish exchanges between banknotes and coins of the Brazilian monetary system, depending on their values
D11 - Solve problems involving the calculation of the perimeter of flat figures, drawn on gridded meshes.
D12 - Solve problems involving calculating or estimating areas of flat figures drawn on gridded meshes.
Length measurements, mass measurements, area measurements, volume measurements, time measurements, angle measurements and the monetary system.

The Drawings represents the cake that Marcos bought.

Use the inverse operation to calculate the value of each box based on information about some cities.

Solve problems by presenting operations and answer in the notebook.

Calculate the value of each of the following numeric expressions.


Subscribe to our email list and receive interesting information and updates in your email inbox
Thanks for signing up.