
O phototropismIt is a movement performed by plants with the stimulus of sunlight. Sun. It can be positive, when the plant is directed in favor of the light stimulus, or negative, when the plant is directed against the light stimulus.
We prepared a list of exercises on phototropism so you can test your knowledge about this plant movement.
see more
Biology teacher fired after class on XX and XY chromosomes;…
Cannabidiol found in common plant in Brazil brings new perspective…
You can consult the feedback and save this list of exercises in PDF at the end of the post!
1) (UEL) When a stem is illuminated unilaterally, it presents positive phototropism due to the accumulation of auxins, which causes:
a) Cell distention on the unilluminated side.
b) cell division on the non-illuminated side.
c) cell distention on the illuminated side.
d) cell division at the apex of the stem.
e) cell division on the light side.
2) (FCC) A potted plant is placed in a horizontal position as shown in the following diagram:
 The root is expected to:
The root is expected to:
a) and the stem stops growing.
b) and the stem continue to grow horizontally.
c) and the stem show positive geotropism.
d) present positive geotropism and the stem, negative geotropism.
e) present negative geotropism and the stem, positive geotropism.
3) (UDESC) The luminosity is a factor of great influence in the growth of the stems, because, normally, they have a growth towards the light, the so-called positive phototropism. Mark the alternative that contains the name of the main plant hormone involved in the positive phototropism of stems.
a) Noradrenaline.
b) Cytosine.
c) Gibberellins.
d) Auxin.
i) Ethylene.
4) (UPF-RS) Some bean seeds were put to germinate in a vase placed on the right, at the bottom of a completely closed box and in the dark. Ten days later, a hole was made in the front, top and left of the box. It was observed that the bean plants, as they grew, began to come out through the hole, describing a curvature (see figure). Test the:
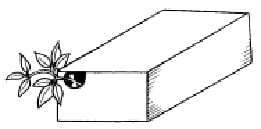 a) photonastism.
a) photonastism.
b) phototropism.
c) geotropism.
d) hydrotropism.
i) thermotropism.
5) Phototropism is called positive when:
a) The plant grows towards the light source.
b) the plant moves toward the light source.
c) the growth of the plant occurs in the opposite direction to the light source.
d) the plant moves in the opposite direction to the light source.
e) plant growth occurs in response to the light source, regardless of direction.
6) (UNIFOR) In a plant illuminated unilaterally, the concentration of auxin on the illuminated side of the stem ____________ and the plant presents ____________.
To make the presented sentence correct, just replace the spaces, respectively, with:
a) increases, positive phototropism.
b) decreases, positive phototropism.
c) increases, negative phototropism.
d) decreases, negative phototropism.
e) decreases, erect growth.
7) A plant was placed inside a box that had only a small opening through which sunlight entered. Over time, the stem was observed to manifest growth towards the light source, a process called:
a) positive photoperiodism.
b) negative photoperiodism.
c) positive phototropism.
d) negative phototropism.
i) gravitropism.
8) (UNIRIO) The figure below illustrates a phenomenon that occurs with vegetables. In this regard, analyze the statements.
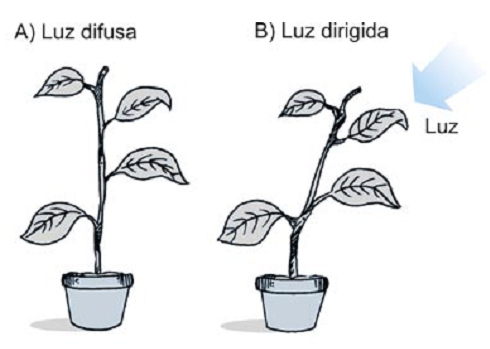 I – The phenomenon shown is due to the activity of auxins.
I – The phenomenon shown is due to the activity of auxins.
II – This phenomenon is given the generic name of phototropism.
III – The plant grows by turning towards the light because it stimulates the production of auxins.
The correct statement(s) is(are):
a) III only.
b) only I and II.
c) only I and III.
d) only II and III.
e) I, II and III.
9) (CESGRANRIO) Cultivating a small plant in a dark environment with a small opening, in order to allow unilateral lighting, it is verified that the plant grows leaning towards the source luminous. Such curvature is explained:
a) by the higher concentration of chlorophyll on the illuminated face.
b) due to the absence of a support tissue, sufficiently developed, capable of keeping the plant in its normal position.
c) by the higher concentration of auxin on the illuminated side, causing greater growth and consequent inclination of the plant.
d) by greater meristematic activity on the illuminated face, resulting from the presence of pigments.
e) due to the unequal distribution of auxin on the light and dark sides of the plant, with a higher concentration of hormones on the dark side.
10) (FUVEST) A plant subjected to unilateral lighting will grow towards the light source, as shown in the scheme.
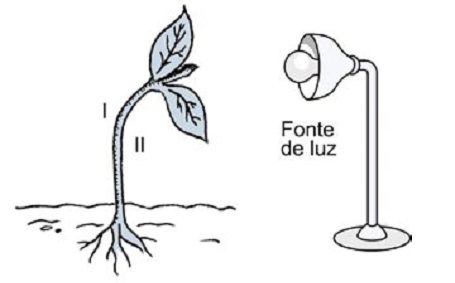 This occurs due to the migration of auxin to:
This occurs due to the migration of auxin to:
a) region I, which causes greater cell division on that side.
b) region II, which causes greater division of cells on the opposite side.
c) the root, which, when growing in the opposite direction to the light, guides the growth of the stem in the opposite direction.
d) region II, which causes greater elongation of the cells on the opposite side.
e) region I, which causes greater elongation of the cells on that side.
1 – the
2 – d
3 – d
4 – b
5 – the
6 – b
7 – c
8 – b
9 and
10 – and
Click here to save this list of exercises on phototropism in PDF!
Read too:


