
A table is a tool used to organize data in rows and columns and allow a better visualization of the information that is being presented.
The use of a table also facilitates the search and identification of information, since we can concentrate our searches on a single row or column, for example.
see more
Students from Rio de Janeiro will compete for medals at the Olympics…
The Institute of Mathematics is open for registration for the Olympics…
However, it is important to emphasize that, to be useful, the tables must be constructed according to what you want to analyze, that is, with some objective. In addition, many times, the ideal is that they are used with graphics.
Tables can be simpler or more complex and with different types of information. However, they all must have some basic elements.
Now, let's see some examples of how to make a table.
Example 1) An elementary school teacher wants to organize her students' grades in math, Portuguese, history, geography, and science.
Student grades are:
Thus, we can build a table with a row for each student and a column for each subject, see:
Notice how much easier it is to visualize each student's performance and compare grades across different students and across disciplines.
Also, note that for each new student that enters the class, the teacher will only need to add a new line in the table and enter the grades of that student.
Example 2) A nutritionist prepared a diet for a patient to follow on each of the working days of the week.
With this data, we can build a table with a row for each meal of the day and a column for each day of the week, see:
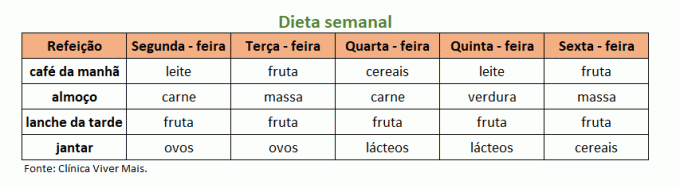
See that if you need to add a diet for the weekend, just create two new columns in the table and insert the meals for Saturday and Sunday.
Note that we could also create a table with the reverse order of rows and columns, that is, in the rows we would have the days of the week and in the columns, the meals.
You may also be interested:


