Activities with length measurements help children to develop techniques for measuring kilometers, centimeters, millimeters, which are widely used in our daily lives.

This activity aims to:
Develop reading and writing skills;
Discovering that in the past people used body parts as a reference to measure lengths;
Construct the meaning of the concept of length measurements;
Identify numbers in different contexts in which they find themselves;
Measure length using non-standard and standardized measurement units;
Recognize standardized length measurement units: meter and centimeter;
Compare measurements and make estimates;
Use oral counting in playful situations (games) and in situations in which they recognize their need;
Communicate quantities using orality, drawing, numerical notation, that is, conventional and unconventional records;
Value exchanges of experiences with colleagues and respect for their and other people's opinions;

To measure length, we use the meter as a unit, which we represent by the symbol m (read meter).

Measures greater than the meter
1000 m = 1 km (kilometer)
100 m = 1 (hectometer)
10 m = 1 dam (decameter)
Measures smaller than the meter
1 m = 10 dm (decimeter)
1 m = 100 cm (centimeter)
1 m = 1000 mm (millimeter)
Don't forget: Symbols are written in lowercase, no dots and no s to indicate the plural.

The content that can be used is:
Measurement and comparison of length measurements using unconventional measurement units (steps, palms, etc.) and conventional (centimeter, meter, kilometer), with different instruments (ruler, measuring tape, etc);
Estimate of length measurements.

Children in early grades can solve problems involving size comparison directly, such as comparing who is the highest of the class, and others that require intermediaries (hands, rulers, measuring tape, etc.), when the objects compared cannot be transported. For example, whether the window is wider than the blackboard.
Propose children to compare whether their classroom's classroom is larger or smaller than another's classroom.

Ask them to calculate how many steps it will take to get from the board to the back of the room. Guide them so that, in this first moment, they make an estimate without directly measuring the room, give an approximate answer and write it down on a sheet of paper.
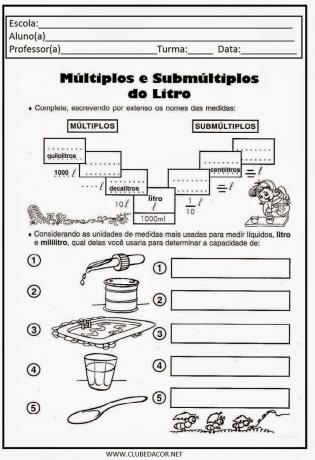


1) Look at the number line below and answer the questions:

a) What numbers are before 6?
A:
b) What numbers are after 6?
A:
c) What numbers are between 4 and 10?
A:
d) Which number comes before 15?
A:
e) Which number comes immediately after 11?
A:
f) Which number comes before 1?
A:
g) What numbers are between 10 and 15?
A:
2) Note the line below:
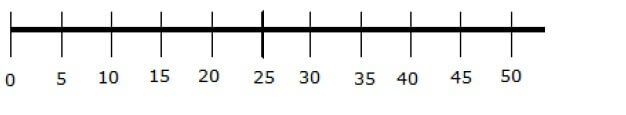
a) What can be observed in this sequence of numbers?
A:
b) Is it possible to mark the number 4 on this line? Because?
A:
3) Look at the line below and answer:
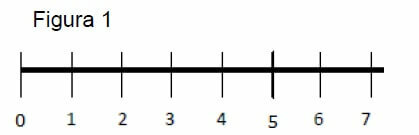
a) Initial number
A:
b) Final number
A:
c) The scale used on the straight is
A:

a) Initial number
A:
b) Final number
A:
c) The scale used on the straight is
A:
Harpy the biggest eagle in the world
The Amazon harpy is the largest eagle in the world. It reaches 90 cm in height and 1.05 m in length from the tip of the tail to the beak. The span of the wing measured from end to end is 1.7 m to 2.1 m. Some of its feathers reach up to 50 cm.
Available in:
4) Answer what are the measurements that appear in the information about the Amazonian harpy eagle?
A:
5) Answer which harpy measures are greater than 1 m?
A:
6) Answer which of the harpy's measurements are less than 1 m?
A:
Did you like it? Share this post on your social network
 ACTIVITIES ON NATURAL NUMBERS FOR THE 4th, 5th and 6th YEAR
ACTIVITIES ON NATURAL NUMBERS FOR THE 4th, 5th and 6th YEAR
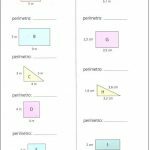 MATHEMATICS ACTIVITIES ON PERIMETER
MATHEMATICS ACTIVITIES ON PERIMETER
 MULTIPLICATION EDUCATIONAL ACTIVITIES
MULTIPLICATION EDUCATIONAL ACTIVITIES
 CALENDAR ACTIVITIES
CALENDAR ACTIVITIES
 MULTIPLE ACTIVITIES OF A NATURAL NUMBER
MULTIPLE ACTIVITIES OF A NATURAL NUMBER
 Math Activities 1st Grade
Math Activities 1st Grade
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed.