
Altogether, planet Earth performs a series of fourteen movements, some of them performed in conjunction with the Solar System, the Milky Way or even the Universe. However, of all these variations, two are of most interest to the practical reality of societies: rotation and translation. After all, the effects of these movements practically condition our daily activities and help us to understand phenomena such as the succession of days and nights and the seasons of the year.
see more
Teacher performance is a key factor for the full inclusion of students…
Financial education is the best ‘medicine’ for chronic indebtedness…
Terrestrial rotation is the movement that the Earth performs around its own axis, which has an inclination of 23º27' in relation to the vertical plane of the planet's orbit. The direction of this movement is west-east, which means that the apparent movement of the sun (in the view of those on the earth's surface) is from east to west.
The main effect of the rotation movement on the dynamics of the planet is the alternating succession of days and nights. However, the duration of each day and each night varies throughout the year, as we will see later, especially if we consider the polar areas of the Earth.
Although, from our point of view, the Earth performs its rotation movement slowly, it occurs at a high speed: 1666 kilometers per hour. With that, our entire huge planet can complete this movement in just 23 hours, 56 minutes and 4 seconds.
The terrestrial translation – also called revolution – is the movement that the Earth performs around the sun, that follows a definite path we call an orbit, just like all the other planets in our solar system. solar. When the Earth completes an entire revolution around the sun, the total year is completed, in terms of time.
The Earth's displacement speed along the translation movement, on average, is approximately 107,000 km/h, so that its cycle, in exact numbers, extends over 365 days and 6 hours. These extra hours not accounted for in the demarcation of years are compensated every four years, when we have the date of February 29 in the so-called “leap year”.
ADVERTISING
See too:The Earth's Internal Structure
In addition to the succession of years, the main effect of the rotation movement is the existence of the seasons. weather, which occur from an alternation of two phenomena called solstices and equinoxes. The four seasons based on this definition are most noticeable in subtropical areas, at high latitudes.
As we have already said, the Earth is not equally illuminated and affected by the sun's rays in all its ranges. latitudianis, with a certain difference in the north-south direction, all because of the inclination of the axis of rotation terrestrial. Thus, as the translational movement progresses throughout the year, we have a difference in way in which the sun's rays fall on the surface, which allows the existence of the seasons of the year.
See the scheme below:
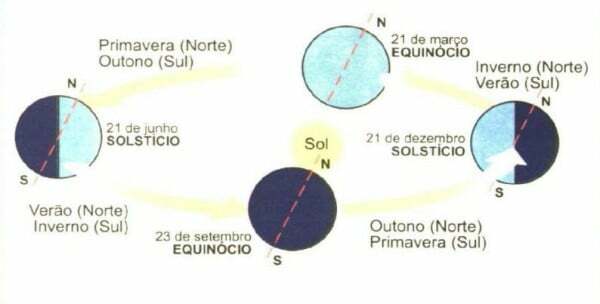
You solstices they are, therefore, the periods of the year when the Earth is illuminated differently between its hemispheres. Thus, in winter, days are shorter than nights, and in summer, days are longer. Likewise, when it is winter in the southern hemisphere it is summer in the north and vice versa.
You equinoxes are, in turn, the periods of the year when the Earth is equally illuminated between its hemispheres, with its apex being reached on dates when days and nights have an equal duration. The equinoxes demarcate spring and autumn in the different hemispheres alternately.
By Rodolfo F. Alves Pena
Master in Geography


